Introduction
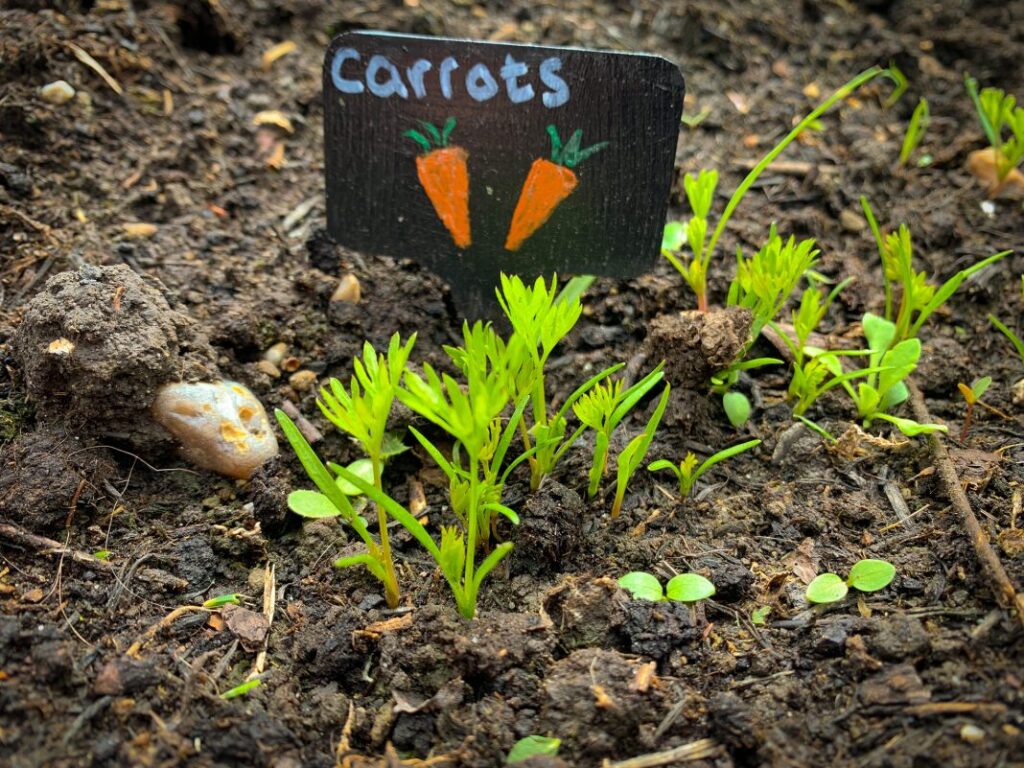
Understanding the sprouting process of carrots is essential for gardeners and enthusiasts alike, as it provides valuable insights into the growth and development of this popular root vegetable. By recognizing the physical characteristics, environmental factors, and common issues associated with carrot sprouting, individuals can effectively monitor and support the growth of their crops. This article aims to delve into the intricacies of what carrots look like when they sprout, offering practical guidance for nurturing healthy and thriving plants.
Physical Characteristics of Sprouting Carrots
Initial Signs of Sprouting
As carrot seeds begin to germinate, several distinct stages mark the onset of sprouting.
Germination Process: Initially, the seed coat softens and absorbs water, triggering biochemical changes that initiate growth.
Emergence of Shoots: Soon after germination, tiny shoots emerge from the soil, seeking sunlight and nutrients.
Formation of Cotyledon Leaves: These initial leaves, known as cotyledons, unfurl from the emerging shoots, providing nourishment to the developing seedling.
Growth Progression
As the sprouting process continues, carrots undergo noticeable growth and development.
Development of True Leaves: Following the emergence of cotyledons, true leaves begin to form, resembling the characteristic foliage of mature carrot plants.
Lengthening of Stems: The stems elongate, lifting the leaves higher above the soil surface in search of light.
Appearance of Root Hairs: Delicate root hairs develop along the growing roots, facilitating water and nutrient absorption from the soil.
Color and Texture Changes
Distinctive changes in color and texture accompany the sprouting of carrots.
Pale Shoots: Initially, the shoots exhibit a pale, tender appearance, gradually gaining strength and vigor as they mature.
Tender Leaves: The young leaves of sprouting carrots are soft and delicate, gradually developing a firmer texture as they expand and mature.
White Roots: Beneath the soil surface, the developing roots appear white and slender, branching out to anchor the plant and absorb essential nutrients.
Environmental Factors Affecting Carrot Sprouting
Temperature
Temperature plays a crucial role in determining the success of carrot sprouting.
Optimal Germination Conditions: Carrot seeds germinate best in soil temperatures ranging from 60 to 70°F (15 to 21°C), ensuring rapid and uniform sprouting.
Impact of Extreme Temperatures: Excessive heat or cold can impede germination and stunt seedling growth, necessitating careful monitoring and adjustment of growing conditions.
Seasonal Variations: Spring and fall are ideal seasons for carrot planting, as moderate temperatures promote robust germination and vigorous growth.
Moisture Levels
Adequate moisture is essential for successful carrot sprouting and seedling establishment.
Importance of Adequate Moisture: Consistent soil moisture promotes hydration and nutrient uptake, facilitating healthy growth and development.
Risks of Overwatering: Excessive moisture can lead to waterlogged soil conditions, increasing the risk of fungal diseases and root rot.
Effects of Drought: Insufficient moisture can hinder germination and stunt seedling growth, emphasizing the need for regular watering during dry spells.
Light Requirements
Light plays a crucial role in photosynthesis and plant growth, influencing carrot sprouting and seedling development.
Role of Light in Photosynthesis: Sunlight provides the energy needed for photosynthesis, fueling the growth of young carrot plants and ensuring robust development.
Germination in Darkness: While carrot seeds do not require light to germinate, adequate illumination is essential once the seedlings emerge to support healthy growth and development.
Need for Proper Lighting: Inadequate light can lead to leggy, weak seedlings with poor vigor, underscoring the importance of providing adequate lighting during the sprouting stage.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding what carrots look like when they sprout is essential for cultivating healthy and productive crops. By recognizing the physical characteristics, monitoring environmental factors, and addressing common issues associated with carrot sprouting, gardeners can optimize growing conditions and support vigorous seedling development. Regular observation, proper care, and timely intervention are key to nurturing strong and resilient carrot plants from seed to harvest. Whether grown in home gardens, allotments, or commercial fields, freshly sprouted carrots offer a delicious and nutritious addition to meals, embodying the rewards of successful cultivation. As we embark on the journey of carrot cultivation, may we approach each stage of growth with diligence, patience, and appreciation for the wonders of nature’s bounty.