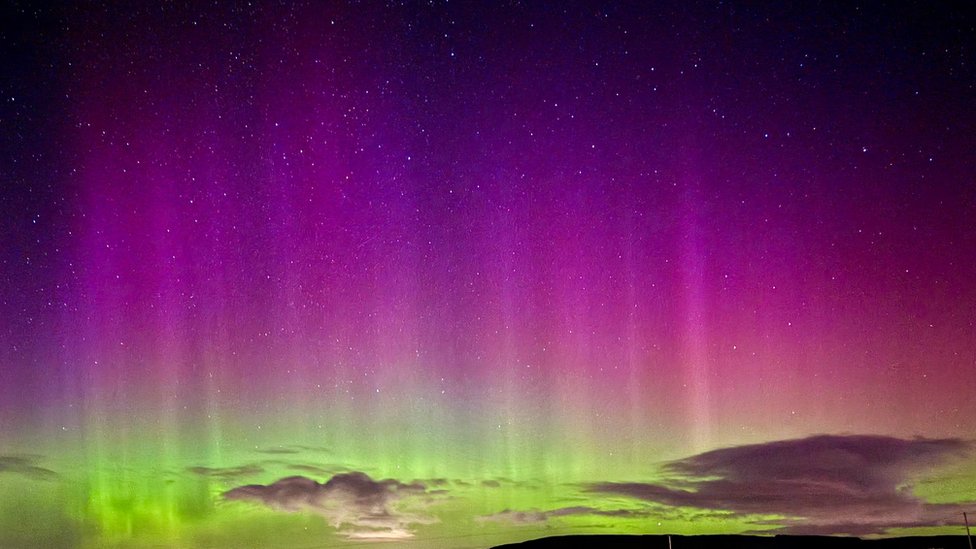
The northern lights, also known as the aurora borealis, have captivated humanity for millennia. Their vibrant curtains of color dancing across the night sky inspire awe and wonder. But what causes this celestial phenomenon, and how can you witness it yourself? This comprehensive guide unravels the science behind the aurora borealis and equips you with the knowledge to plan your own unforgettable aurora-chasing adventure.
A Cosmic Ballet: Understanding the Aurora Borealis (Northern lights)
The aurora borealis is a dazzling display of light produced by the interaction between Earth’s magnetic field and energetic particles from the sun. Our sun constantly releases a stream of charged particles called the solar wind, primarily electrons and protons, hurtling towards Earth at incredible speeds. Fortunately, Earth’s magnetic field acts as a giant shield, deflecting most of the solar wind around the poles.
However, during periods of high solar activity, such as solar flares and coronal mass ejections, particularly strong solar winds can overwhelm the magnetic field. These energetic particles get channeled towards the poles along the magnetic field lines. Upon reaching the upper atmosphere (thermosphere), they collide with atoms and molecules, transferring their energy. The excited atoms and molecules then release this energy as light, creating the mesmerizing auroral displays.
The color of the aurora depends on the type of gas molecule that’s been energized. Collisions with oxygen atoms typically produce greenish-yellow auroras, while nitrogen creates shades of red and blue. The intensity and form of the aurora also vary depending on the energy and direction of the incoming solar wind particles.
Where the Lights Dance: Prime Locations for Viewing the Aurora Borealis
The aurora borealis is primarily visible in a region known as the auroral oval, a ring-shaped zone centered around the Earth’s magnetic poles. Your best bet for witnessing the northern lights falls within this auroral oval, encompassing areas in:
- Northern Canada
- Alaska
- Greenland
- Iceland
- Norway
- Sweden
- Finland
- Russia
While the aurora can be seen throughout the year, its frequency and intensity increase significantly during periods of high solar activity, which peak roughly every 11 years. Within these cycles, the best time for aurora viewing typically falls around the equinoxes (spring and fall). During these times, the tilt of Earth’s axis allows for a more direct interaction between the solar wind and the magnetic field at the poles, leading to a higher chance of auroral displays.
Maximizing Your Aurora Borealis Adventure
Planning a trip to witness the aurora borealis? Here are some key tips to increase your chances of success:
-
Head North: The further north you travel within the auroral oval, the higher the likelihood of witnessing the aurora.
-
Target Solar Activity: Research upcoming solar forecasts and aim your trip to coincide with periods of increased solar wind activity, typically around the equinoxes.
-
Seek Out Darkness: Light pollution significantly diminishes the visibility of the aurora. Look for locations with minimal artificial light sources, preferably far from major cities.
-
Embrace the Cold: Auroral displays typically occur in colder regions. Be prepared for winter weather with appropriate clothing and gear.
-
Patience is Key: The aurora is a natural phenomenon, and sightings aren’t guaranteed on any given night. Clear skies and a little patience can go a long way.
Witnessing the Spectacle: What to Expect
The aurora borealis can manifest in a variety of awe-inspiring forms, from wispy streaks and shimmering arcs to vibrant curtains and dancing veils of light. The colors can range from vibrant greens and yellows to deep reds and blues. The intensity of the display can also vary, with some auroras being faint and subtle, while others explode with color and movement.
Capturing the Magic: Photography Tips for the Aurora Borealis
If you’re fortunate enough to witness the aurora borealis, you might want to capture this celestial wonder with your camera. Here are some tips for stunning aurora photography:
-
Embrace a DSLR: A DSLR camera with a manual mode and a wide-angle lens allows you to capture the aurora’s details and movement effectively.
-
Minimize ISO: While tempting to boost the ISO for a brighter image, it will also introduce unwanted noise. Experiment with longer shutter speeds to capture sufficient light without sacrificing image quality.
-
Steady with a Tripod: Long exposure times are necessary to capture the aurora’s faint light. A sturdy tripod will ensure your images remain sharp and clear.
-
Compose with the Foreground: Incorporate interesting foreground elements like trees, mountains, or a cabin into your composition to add depth and context to your aurora photos.
The Enduring Allure: The Aurora Borealis Beyond the Spectacle
The aurora borealis is more than just a beautiful lightshow; it’s a powerful reminder of our connection to the sun and the dynamic processes at play in our solar system. Witnessing this celestial ballet can spark a sense of wonder and inspire a deeper appreciation for the natural world.
Responsible Aurora Chasing: Respecting the Environment
As the popularity of aurora tourism rises, it’s crucial to practice responsible travel habits. Here are some ways to minimize your environmental impact while chasing the lights:
-
Choose Eco-Friendly Accommodations: Opt for accommodations with sustainable practices, such as locally sourced food and energy-efficient buildings.
-
Minimize Transportation Emissions: Consider carpooling or utilizing public transportation options whenever possible.
-
Leave No Trace: Respect the delicate ecosystems of the aurora viewing regions. Pack out all trash and avoid disturbing wildlife.
The Call of the Aurora: Frequently Asked Questions
FAQ on the Northern Lights
-
Is it safe to be under the aurora borealis? Absolutely! The aurora borealis is a harmless phenomenon caused by natural light emissions high in the atmosphere.
-
Can you hear the aurora borealis? No, the aurora borealis is a visual phenomenon and doesn’t produce any audible sound.
-
What are some aurora borealis tours available? Many reputable tour operators offer guided aurora-chasing adventures. These tours often include transportation, accommodation, and experienced guides who can help you maximize your chances of witnessing the lights.
-
Are there any online resources for tracking auroral activity? Yes, several websites and smartphone apps provide real-time information on solar wind activity and aurora forecasts. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) is a valuable resource for aurora borealis forecasts.
Embrace the Adventure: A Journey Under the Dancing Lights
The aurora borealis beckons with its captivating display of light and color. By understanding the science behind this phenomenon, planning your trip strategically, and practicing responsible travel habits, you can embark on an unforgettable adventure to witness nature’s celestial masterpiece. So, pack your warm clothes, grab your camera, and get ready to be awestruck by the magic of the aurora borealis.
Read about: Where Do Old Satellites Go When They Die?