The Space, the vast and mysterious expanse that stretches infinitely beyond the confines of Earth’s atmosphere, has been a subject of fascination for humanity for millennia. From ancient civilizations observing the night sky to modern-day space exploration missions, our curiosity about the universe has been a driving force behind scientific discovery, technological innovation, and a profound sense of wonder. In this article, we explore the significance of space exploration, its impact on science and society, and the future of humanity’s journey beyond Earth.
The Early Fascination with The Space
Humanity’s fascination with the stars dates back to ancient times. Early astronomers and cultures around the world sought to understand the celestial bodies and their movements. The Babylonians, Egyptians, Greeks, and Mayans all created elaborate systems to track the stars, planets, and other celestial phenomena. The ancient Greeks, for example, developed early theories about the nature of the universe, with thinkers like Aristotle and Ptolemy positing that the Earth was the center of the universe.
However, it wasn’t until the 16th and 17th centuries that groundbreaking discoveries fundamentally changed our understanding of space. The work of Copernicus, Galileo, and Kepler shattered the geocentric model and set the stage for modern astronomy. The heliocentric theory, which posited that the Earth orbited the Sun, replaced the long-held belief that the Earth was the center of the universe. This marked the beginning of a new era of exploration, both intellectually and eventually physically.
The Space Age and the Birth of Modern Exploration
The real breakthrough in human exploration of The Space began in the mid-20th century, during what is now known as the Space Age. The launch of the Soviet satellite Sputnik 1 on October 4, 1957, marked the beginning of humanity’s direct engagement with space. The success of Sputnik demonstrated that space was no longer a distant realm of speculation, but a frontier that could be accessed and explored with the right technology.
The race to explore space intensified as the United States and the Soviet Union entered into the Cold War, and space became a new arena for political and technological competition. In 1961, Soviet cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin became the first human to journey into space, orbiting the Earth aboard Vostok 1. His historic flight was followed by the United States’ Mercury and Gemini programs, which laid the groundwork for more ambitious space exploration missions.
The pinnacle of The Space exploration during this period was the Apollo program. In 1969, Apollo 11 successfully landed American astronauts Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin on the Moon, with Armstrong’s iconic words, “That’s one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind,” marking the achievement of one of humanity’s greatest accomplishments. The Apollo missions not only demonstrated the potential of human space exploration but also ignited public interest in the study of space and the sciences.
The Internationalization of The Space Exploration
Since the Apollo era, space exploration has become more collaborative, with numerous countries and organizations contributing to the advancement of The Space technology. The International Space Station (ISS), a joint project involving the United States, Russia, Europe, Japan, and Canada, has served as a symbol of international cooperation. Launched in 1998, the ISS orbits the Earth at an average altitude of 400 kilometers and serves as a microgravity research laboratory. It provides scientists from around the world with the opportunity to conduct experiments in a unique environment that cannot be replicated on Earth.
The ISS is also a testament to humanity’s ability to work together on complex scientific and engineering challenges. The station’s modules, equipment, and research projects are the result of years of planning, investment, and effort from many nations. The cooperation required to build and maintain the ISS has provided valuable lessons for future endeavors in space exploration, including the potential for missions to Mars and beyond.
Technological Innovations and the Impact of Space Exploration
Space exploration has not only expanded our knowledge of the universe but has also led to numerous technological innovations that have had practical applications on Earth. The technology developed for space missions has often found its way into consumer products and industries, improving life on our planet.
For instance, the development of miniaturized electronics for spacecraft led to the creation of more efficient and powerful computers, which in turn revolutionized industries ranging from telecommunications to healthcare. Satellite technology, which was initially developed for space exploration, is now integral to GPS systems, weather forecasting, global communications, and even agriculture.
The research conducted in The Space also has direct benefits for human health. For example, the study of how the human body reacts to microgravity has helped scientists understand the effects of bone density loss and muscle atrophy, leading to advances in treatments for conditions like osteoporosis. Furthermore, materials developed for space applications, such as lightweight, durable fabrics and heat-resistant materials, have been adapted for use in everything from medical devices to protective clothing.
The Search for Life Beyond Earth
One of the most profound questions that space exploration seeks to answer is whether life exists beyond Earth. For centuries, the notion that other worlds could harbor life has captured the human imagination. The discovery of exoplanets—planets orbiting stars outside our solar system—has significantly expanded the potential for finding extraterrestrial life. As of 2023, scientists have confirmed the existence of over 5,000 exoplanets, many of which are located in the “habitable zone” of their stars, where conditions may be right for liquid water to exist.
NASA’s Perseverance rover, which landed on Mars in 2021, is conducting a series of experiments to determine whether microbial life ever existed on the Red Planet. The rover is exploring the surface of Mars, collecting samples, and sending data back to Earth. The upcoming missions to moons like Europa and Enceladus—two of Jupiter’s and Saturn’s moons—are particularly exciting because they may harbor subsurface oceans beneath their icy crusts, environments that could potentially support microbial life.
The search for extraterrestrial life continues to be one of the most compelling drivers of space exploration. Whether or not we find definitive evidence of life beyond Earth, the very search for it challenges our understanding of biology, chemistry, and the conditions necessary for life to thrive.
The Future of Space Exploration
Looking to the future, space exploration is poised to enter a new phase. Private companies like SpaceX, Blue Origin, and others are rapidly advancing technologies that will make space more accessible than ever before. SpaceX’s Starship, for instance, is designed to be a fully reusable spacecraft that could one day carry humans to Mars and beyond. Meanwhile, the growing interest in space tourism could allow private citizens to experience space travel, opening up new frontiers for commercial ventures in space.
Another exciting prospect is the potential for permanent human settlements on other planets. NASA’s Artemis program aims to return humans to the Moon by the mid-2020s, with the goal of establishing a sustainable human presence there by the 2030s. The Moon could serve as a stepping stone for future missions to Mars and other distant destinations in the solar system. Meanwhile, the development of advanced propulsion systems, such as nuclear thermal propulsion, could significantly reduce travel time to distant planets.
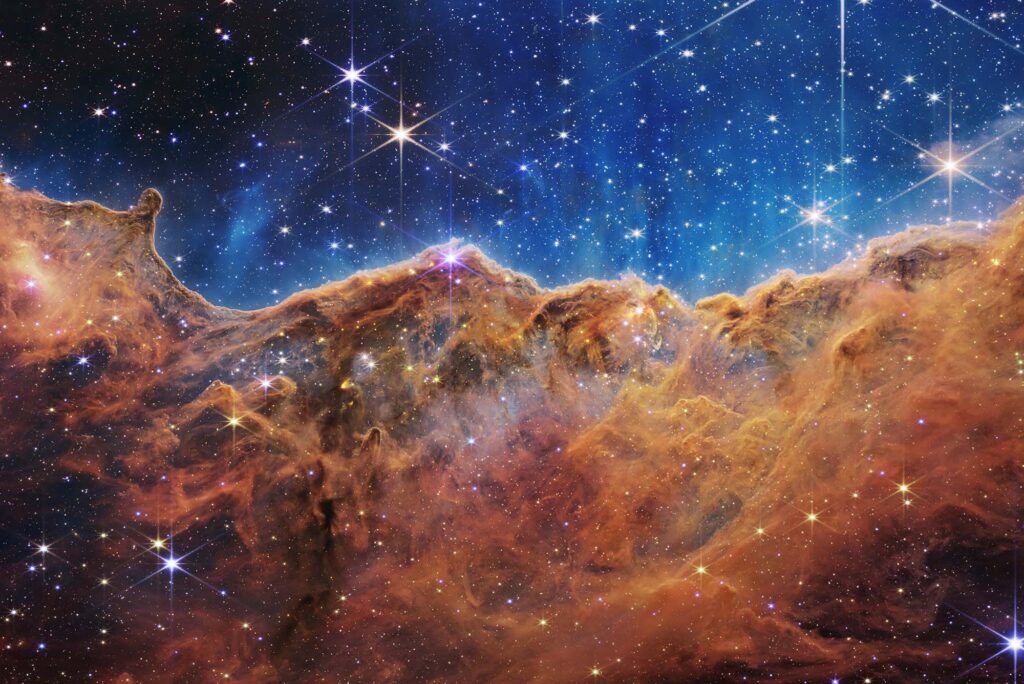
The future of space exploration also holds the promise of new scientific discoveries. The James Webb Space Telescope, launched in 2021, is already revealing breathtaking images of distant galaxies, nebulae, and stars. Its advanced capabilities are expected to revolutionize our understanding of the origins of the universe, the formation of planets, and the conditions for life in the cosmos.
Conclusion
Space exploration is one of humanity’s most ambitious and inspiring endeavors. From the early observations of the stars to the launching of spacecraft and the search for life on distant planets, our curiosity about the universe continues to propel us forward. The advancements made in space technology have not only expanded our understanding of the cosmos but have also improved life on Earth in countless ways. As we look to the future, the possibilities for exploration and discovery seem limitless. Space, with all its mysteries, remains an enduring testament to humanity’s relentless quest for knowledge and adventure.